I – Introduction
II– How to Fix if RAID seems “In Degreed”
III– How to Fix if RAID seems “Unmounted”
IV – How to Fix if RAID seems Not Active (New way to fix!)
V – RAID HDD order seems wrong just like “RAID 5 – Drives : 2 4 3″and device seems Not Active
VI – How to Fix if RAID seems as “Single Disk”
VII – User Remove the RAID Volume
VIII – How to Fix if 2 HDD gives error on RAID 5, 3 HDD gives error on RAID 6
IX – Raid fail – HDDs have no partitions;
X – RAID fail – Partitions have no md superblock
XI – No md0 for array
XII – NAS fail –MountHDD(s)with another QNAP NAS
I – Introduction;
Warning : This documents are recomended for Professional users only. If you dont know what you’r doing, you may damage your RAID which cause loosing data. Qnapsupport Taiwan works great to solve this kind of RAID corruptions easly, and My advice is directly contact with them at this kind of cases.
You can download QNAP NAS Data Recovery Document Down Below:
QNAP_NAS_Data_Recovery
NAS is OK but cannot access data
raidtab is broken or missing
Check raid settings and configure right raidtab
•HDD have no partitions
Use parted to recreate the partitions
•Partitions have no MD superblock
mdadm -CfR –assume-clean
•RAID array can’t be assembled or status is inactive
check above and make sure every disks on raid exist
•RAID array can’t been mounted
e2fsck, e2fsck -b
•Able to mount RAID but data is disappear
umount and e2fsck, if not work, try data recovery
•RAID is in degraded, read-only
backup the data then mdadm -CfR, it not work, recreate the RAID
NAS fail
MountHDD(s)with another QNAP NAS (System Migration)
MountHDD(s)with PC ( R-Studio/ ext3/4 reader) (3rd party tool )
Data are deleted by user/administrator accidentally
data recovery company, photorec, r-studio/r-linux
Introduction of mdadm command
#mdadm -E /dev/sda3 > that will tell if it is md disk
#mdadm -Af /dev/md0 /dev/sd[a-d]3 > that will get available md disk into raid array
———————————–
#mdadm -CfR -l5 -n8 –assume-clean /dev/md0 /dev/sd[a-h]3 > that will overwrite the mdstat on each disk
> -CfR force to create the raid array
> -l5 = raid 5array
> -n8 = available md disk
> –assume-clean without data partition syncing
Introduction of Two Scripts;
# config_util
Usage: config_util input
input=0: Check if any HD existed.
input=1: Mirror ROOT partition.
input=2: Mirror Swap Space (not yet).
input=4: Mirror RFS_EXT partition.
>> usually we have config_util 1 to get the md9 ready
# storage_boot_init
Usage: storage_boot_init phase
phase=1:mountROOTpartition.
phase=2: mount DATA partition, create storage.conf and refresh disk.
phase=3: Create_Disk_Storage_Conf.
>> usually we have storage_boot_init 1 to mount the md9
II -How to Fix if RAID seems “In Degreed”
If your RAID system seems as down below, use this document. If not, Please dont try anything in this document:
A – Qnap FAQ Advice;
Login to Qnap. Disk Managment ->Volume managment. One of your HDD should give “Read/write” or “Normal” error, or Qnap doesnt Recognize there is a HDD on on slot.
Just plug out Broken HDD, wait over 20 seconds, and plug in new HDD. If more than one HDD seems broken, dont change 2 HDD at the same time. Wait Qnap finish to Synronize first HDD, and after it completes, change other broken HDD.
If you loose more HDD than RAID HDD lost tolarance, Backup your datas quickly to another Qnap or External HDD.
Note : New HDD must be same size with your other HDDs. Qnap doesnt accept lower size new HDD. Also I dont advice to use Higher size HDD at this kind of cases. You can use another brand of HDD, or differen sata speed HDDs.
Also, If your HDD seems doesnt plugged in HDD port even if you change it with a new one, it may be an Hardware problem about Qnap sata cable or Mainboard. Send device for Repair to vendor, or open device and plug out sata cable from mainboard, then plug it back.
B – Qnap RAID Recovery Document;
RAID fail – RAID is degraded, read-only
•When degraded, read-only status, there is more disk failure than the raid can support, need to help the user to check which disks are faulty if Web UI isn’t helpful
– Check klog or dmesg to find the faulty disks
•Ask user to backup the data first
•If disks looks OK, after backup, try “mdadm -CfR –assume-clean” to recreate the RAID
•If above doesn’t work, recreate the RAID
C – My Advice;
If your system seems In Degraded, Failed Drive X, you probably loose more HDD thatn RAID tolerated, so Take your Backup, and Re-Install Qnap From Begining.
III – How to Fix if RAID Becomes “Unmounted”
If your RAID system seems as down below, fallow this document. If not, Please dont try anything in this document:
IF YOU HAVE CRİTİCAL DATA ON QNAP, PLEASE CONTACT WİTH QNAP TAIWAN SUPPORT
A – Qnap FAQ Solution;
Q : My NAS lost all its settings, and all HDDs are shown as unmounted.
A : In case of corrupt/lost config:
1. Power off the NAS. Remove the HDD(s)
2. Power on the NAS
3. After a short beep and a long beep, plug the HDD back into the NAS
4. Run QNAP Finder, it will find the NAS, do NOT configure it!
5. Connect to the NAS by telnet port 13131 (e.g. with Putty)
6. Run the MFA Degree following commands to recover with default config
Use the following commands if using 1 drive (if you have more than 1 HDD, please skip this document)
#mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
# cd /mnt/.config/
# cp /etc/default_config/uLinux.conf /mnt/.config/
# reboot
Use the following command if using 2 drives (not tested) (if you have more than 2 HDD, please skip this document)
# mdadm -A /dev/md9 /dev/sda1 /dev/sdb1
# mount /dev/md9 /mnt
# cd /mnt/.config/
# cp /etc/default_config/uLinux.conf /mnt/.config/
# reboot
8. Above procedure will reset the configuration back to default and then you need to reconfigure it. But all the share should be available now.
Please remember NOT to re-initialize the HDD. Since this will format your HDD and all your data will be lost.
9. To be prepared next time this happens, always make sure you have a working backup of your personal uLinux.conf!
Note: uLinux.conf is the main settings configuration
Taken From : Qnap FAQ
If you have 4 or more HDD, fallow this document. Dont start Qnap wihtout HDDs just like first 2 documents:
RAID fail – Cann’t be mounted, status unmount
(from Offical Qnap RAID recovery document)
1. Make sure the raid status is active (more /proc/mdstat)
2. try manually mount
# mount /dev/md0 /share/MD0_DATA -t ext3
# mount /dev/md0 /share/MD0_DATA -t ext4
# mount /dev/md0 /share/MD0_DATA -o ro (read only)
3. use e2fsck / e2fsck_64 to check
# e2fsck -ay /dev/md0 (auto and continue with yes)
4. If there are many errors when check, memory may not enough, need to create more swap space;
Use the following command to create more swap space
[~] # more /proc/mdstat
…….
md8 : active raid1 sdh2[2](S) sdg2[3](S) sdf2[4](S) sde2[5](S) sdd2[6](S) sdc2[7](S) sdb2[1] sda2[0]
530048 blocks [2/2] [UU]
……….
[~] # swapoff /dev/md8
[~] # mdadm -S /dev/md8
mdadm: stopped /dev/md8
[~] # mkswap /dev/sda2
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 542859 kB
no label, UUID=7194e0a9-be7a-43ac-829f-fd2d55e07d62
[~] # mkswap /dev/sdb2
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 542859 kB
no label, UUID=0af8fcdd-8ed1-4fca-8f53-0349d86f9474
[~] # mkswap /dev/sdc2
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 542859 kB
no label, UUID=f40bd836-3798-4c71-b8ff-9c1e9fbff6bf
[~] # mkswap /dev/sdd2
Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 542859 kB
no label, UUID=4dad1835-8d88-4cf1-a851-d80a87706fea
[~] # swapon /dev/sda2
[~] # swapon /dev/sdb2
[~] # swapon /dev/sdc2
[~] # swapon /dev/sdd2
[~] # e2fsck_64 -fy /dev/md0
If there is no file system superblock or the check fail, you can try backup superblcok.
1. Use the following command to find backup superblock location
# /usr/local/sbin/dumpe2fs /dev/md0 | grep superblock
Sample output:
Primary superblock at 0, Group descriptors at 1-6
Backup superblock at 32768, Group descriptors at 32769-32774
Backup superblock at 98304, Group descriptors at 98305-98310
..163840…229376…294912…819200…884736…1605632…2654208…4096000… 7962624… 11239424… 20480000…
23887872…71663616…78675968..102400000..214990848..512000000…550731776…644972544
2. Now check and repair a Linux file system using alternate superblock # 32768:
# e2fsck -b 32768 /dev/md0
Sample output:
fsck 1.40.2 (12-Jul-2007)
e2fsck 1.40.2 (12-Jul-2007)
/dev/sda2 was not cleanly unmounted, check forced.
Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizescf
…….
Free blocks count wrong for group #241 (32254, counted=32253).
Fix? yes
………
/dev/sda2: ***** FILE SYSTEM WAS MODIFIED *****
/dev/sda2: 59586/30539776 files (0.6% non-contiguous), 3604682/61059048 blocks
3. Now try to mount file system using mount command:
# mount /dev/md0 /share/MD0_DATA -t ext4
RAID fail – able to mount but data disappear
•If the mount is OK, but data is disappear, unmount the RAID and run e2fsck again (can try backup superblock)
•If still fail, try data recovery program (photorec, R-Studio) or contact data recovery company
IV – How to Fix if RAID seems Not Active
If your RAID system seems as the picture down below, fallow this document. If not, Please dont try anything in this document:
Update your Qnap fimware with Qnapfinder 3.7.2 or higher firmware. Just go to Disk Managment -> RAID managment. Choose your RAID and press “Recover” to fix.
If this doesnt work and “Recover” button is still avaible, just fullow these steps;
While device is still working, Plug out HDD that you suspect which maybe broken, and press Recover button again.
Plug out 1.st HDD, Press Recover. If doesnt work, Plug in HDD again, and try same steps for 2.th HDD.
IF THIS DOESTN WORK, PLUG IN THESE HDD BACK AGAİN, AND PRESS RECOVER.
Now, Plug out another HDD and press “Recover” Button again.
IF THIS DOESTN WORK, PLUG IN THESE HDD BACK AGAİN, AND PRESS RECOVER.
I was able to fix my 2 costumers RAID system by whis way, without typing any linux commands.
But must warn you again, best choice is Requesting help from Qnap Taiwan Support Team.
Ofcourse, this may doesnt work. here is another case how I fix;
First, I try to fix “Recovery” method, but doesnt work. At Qnap RAID managment menu, I check All HDDs, But all of them seems good. So I Login with Putty, and type these commands;
mdadm -E /dev/sda3
mdadm -E /dev/sdb3
mdadm -E /dev/sdc3
mdadm -E /dev/sdd3
Except first HDD, other 3 HDD’s doesn have md superblock; Also I try “config_util 1” & “storage_boot_init 2” commands, but both of them gives error;
Costumer got RAID 5 (-l 5) with 4 HDD (-n 4), so ı type this command;
# mdadm -CfR –assume-clean /dev/md0 -l 5 -n 4 /dev/sda3 /dev/sdb3 /dev/sdc3
/dev/sdd3
then mount with this command;
# mount /dev/md0 /share/MD0_DATA -t ext4
And works perfect.
Also here is Putty Steps;
login as: admin
admin@192.168.101.16′s password:
[~] # mdadm -E /dev/sda3
/dev/sda3:
Magic : a92b4efc
Version : 00.90.00
UUID : 2d2ee77d:045a6e0f:438d81dd:575c1ff3
Creation Time : Wed Jun 6 20:11:14 2012
Raid Level : raid5
Used Dev Size : 1951945600 (1861.52 GiB 1998.79 GB)
Array Size : 5855836800 (5584.56 GiB 5996.38 GB)
Raid Devices : 4
Total Devices : 4
Preferred Minor : 0
Update Time : Fri Jan 11 10:24:40 2013
State : clean
Active Devices : 4
Working Devices : 4
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 0
Checksum : 8b330731 – correct
Events : 0.4065365
Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 64K
Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
this 0 8 3 0 active sync /dev/sda3
0 0 8 3 0 active sync /dev/sda3
1 1 8 19 1 active sync /dev/sdb3
2 2 8 35 2 active sync /dev/sdc3
3 3 8 51 3 active sync /dev/sdd3
[~] # mdadm -E /dev/sdb3
mdadm: No md superblock detected on /dev/sdb3.
[~] # mdadm -CfR –assume-clean /dev/md0 -l 5 -n 4 /dev/sda3 /dev/sdb3 /dev/sdc3 /dev/sdd3
mdadm: /dev/sda3 appears to contain an ext2fs file system
size=1560869504K mtime=Fri Jan 11 10:22:54 2013
mdadm: /dev/sda3 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices=4 ctime=Wed Jun 6 20:11:14 2012
mdadm: /dev/sdd3 appears to contain an ext2fs file system
size=1292434048K mtime=Fri Jan 11 10:22:54 2013
mdadm: array /dev/md0 started.
[~] # more /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [linear] [raid0] [raid1] [raid10] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4] [multipath]
md0 : active raid5 sdd3[3] sdc3[2] sdb3[1] sda3[0]
5855836800 blocks level 5, 64k chunk, algorithm 2 [4/4] [UUUU]
md4 : active raid1 sda2[2](S) sdd2[0] sdc2[3](S) sdb2[1]
530048 blocks [2/2] [UU]
md13 : active raid1 sda4[0] sdc4[3] sdd4[2] sdb4[1]
458880 blocks [4/4] [UUUU]
bitmap: 0/57 pages [0KB], 4KB chunk
md9 : active raid1 sda1[0] sdc1[3] sdd1[2] sdb1[1]
530048 blocks [4/4] [UUUU]
bitmap: 1/65 pages [4KB], 4KB chunk
unused devices:
[~] # mount /dev/md0 /share/MD0_DATA -t ext4
[~] #
Here is Result;
Qnap Taiwan Advice:
IF YOU HAVE CRİTİCAL DATA ON QNAP, PLEASE CONTACT WİTH QNAP TAIWAN SUPPORT
RAID fail – RAID can’t be assembled or status is inactive:
1.Check partitions, md superblock status
2.Check if there is any RAID disk missing / faulty
3. Use “mdadm -CfR –assume-clean” to recreate the RAID
V – RAID HDD order seems wrong just like “RAID 5 – Drives : 2 4 3″and device seems Not Active
If your RAID order seems like this:
First try RAID recovery. İf its still failes:
Follow this document:
Download Winscp and Login to your Qnap. Go to etc -> raidtab and first take bakup of this file!
Then double click on this file. At this table, sda means your first HDD, sdb is your second and sdc means your 3.th HDD, and their order seems wrong.
Right table should be like down below so modify RAID like this:
RAID-5
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level 5
nr-raid-disks 3
nr-spare-disks 0
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
device /dev/sdc3
raid-disk 2
At this case I have 4 HDD, so modify nr-raid-disks 4 and also add this line :
device /dev/sdd3
raid-disk 3
It should be look like this:
Now, save this file, and restart your Qnap.
VI – “How to Fix” if all of your HDDs seems as “Single Disk” even you have a RAID structure or accedently RAID Removed;
I Highly Recomanded you to contact with Qnap SupportTaiwan, but I you know what you are doing, here is how to fix document;
RAID Issue – raidtab is broken
•raidtab is used to check if the disk is in RAID group or single and show the RAID information on web UI.
•If the disk is in RAID but Web UI show it is single, or the RAID information is different to the actual disk RAID data ( checked by mdadm -E), then the raidtab should be corrupt. Then you need to manually edit the raidtab file to comply the actual RAID status.
•Check the following slides for raidtab contents
Single
No raidtab
RAID 0 Stripping
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level 0
nr-raid-disks 2
nr-spare-disks 0
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
RAID-1 Mirror
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level 1
nr-raid-disks 2
nr-spare-disks 0
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
JBOD Linear
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level linear
nr-raid-disks 3
nr-spare-disks 0
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
device /dev/sdc3
raid-disk 2
RAID-5
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level 5
nr-raid-disks 3
nr-spare-disks 0
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
device /dev/sdc3
raid-disk 2
RAID-5 + Hot spare
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level 5
nr-raid-disks 3
nr-spare-disks 1
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
device /dev/sdc3
raid-disk 2
device /dev/sdd3
spare-disk 0
RAID-5 + Global Spare
raidtab is same as RAID-5
On uLinux.conf, add a line if global spare disk is disk 4:
[Storage]
GLOBAL_SPARE_DRIVE_4 = TRUE
RAID-6
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level 6
nr-raid-disks 4
nr-spare-disks 0
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
device /dev/sdc3
raid-disk 2
device /dev/sdd3
raid-disk 3
RAID-10
raiddev /dev/md0
raid-level 10
nr-raid-disks 4
nr-spare-disks 0
chunk-size 4
persistent-superblock 1
device /dev/sda3
raid-disk 0
device /dev/sdb3
raid-disk 1
device /dev/sdc3
raid-disk 2
device /dev/sdd3
raid-disk 3
VII – User Remove the RAID Volume
# more /proc/mdstat
**Check if the RAID is really removed
# mdadm -E /dev/sda3
** Check if the MD superblock is really removed
# mdadm -CfR –assume-clean /dev/md0 -l 5 -n 3 /dev/sda3 /dev/sdb3 /dev/sdc3
**Create the RAID, assume it is 3 HDDs raid-5
# e2fsck -y /dev/md0
**check file system, Assume “yes” to all questions. If 64-bit, e2fsck_64
# mount /dev/md0 /share/MD0_DATA -t ext4
** mount the RAID back
# vi raidtab
** manually create the raid table
# reboot
** Need to add the removed network share(s) back after reboot
VIII – How to Fix if 2 HDD gives error on RAID 5, 3 HDD gives error on RAID 6
If you cant reach your datas on Qnap, Plug HDDs to another Qnap (I save my 2 costumer all of datas by this way before)
If you can reach your datas, Quickly Backup your datas to another Qnap or External Drive. After it completes, Install Qnap RAID System again.
IX – Raid fail – HDDs have no partitions;
When use the following commands to check the HDD, there is no partition or only one partition.
# parted /dev/sdx print
The following is sample.
# blkid ** this command show all partitions on the NAS
Note: fdisk -l cannot show correct partition table for 3TB HDDs
The following tool (x86 only) can help us to calculate correct partition size according to the HDD size. Please save it in your NAS (x86 model) and make sure the file size is 10,086 bytes.
ftp://csdread:csdread@ftp.qnap.com/NAS/utility/Create_Partitions
1. Get every disk size:
# cat /sys/block/sda/size
625142448
2. Get the disk partition list. It should contain 4 partitions if normal;
# parted /dev/sda print
Model: Seagate ST3320620AS (scsi)
Disk /dev/sda: 320GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: msdos
Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
1 32.3kB 543MB 543MB primary ext3 boot
2 543MB 1086MB 543MB primary linux-swap(v1)
3 1086MB 320GB 318GB primary ext3
4 320GB 320GB 510MB primary ext3
3. Run the tool in your NAS to get the recover commands:
# Create_Partitions /dev/sda 625142448
/dev/sda size 305245
disk_size=625142448
/usr/sbin/parted /dev/sda -s mkpart primary 40s 1060289s
/usr/sbin/parted /dev/sda -s mkpart primary 1060296s 2120579s
/usr/sbin/parted /dev/sda -s mkpart primary 2120584s 624125249s
/usr/sbin/parted /dev/sda -s mkpart primary 624125256s 625121279s
If the disk contains none partition, run the 4 commands.
If the disk contains only 1 partition, run the last 3 commands.
If the disk contains only 2 partition, run the last 2 commands.
If the disk contains only 3 partition, run the last 1 commands.
4. Check the disk partition after recover. And it should contain 4 partitions now.
# parted /dev/sda print
Model: Seagate ST3320620AS (scsi)
Disk /dev/sda: 320GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: msdos
Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
1 32.3kB 543MB 543MB primary ext3 boot
2 543MB 1086MB 543MB primary linux-swap(v1)
3 1086MB 320GB 318GB primary ext3
4 320GB 320GB 510MB primary ext3
5. Please then run “sync” or reboot the NAS for the new partition to take effect.
X – RAID fail – Partitions have no md superblock
•If one or all HDD partitions are lost, or the partitions have no md superblock for unknown reason, use the mdadm -CfR command to recreate the RAID.
# mdadm -CfR –assume-clean /dev/md0 -l 5 -n 4 /dev/sda3…
Note:
1.Make sure the disk is in correct sequence. Use “mdadm -E” or check raidtab to confirm
2.If one of the disk is missing or have problem, replace the disk with “missing”.
For example:
# mdadm -CfR –assume-clean /dev/md0 -l 5 -n 4 /dev/sda3 missing /dev/sdc3 /dev/sdd3
XI – No md0 for array
manually create the md0 with mdadm -CfR
XII – NAS fail – Mount HDD(s) with another QNAP NAS
•User can plug the HDD(s) to another same model name NAS to access the data
•User can plug the HDD(s) to other model name NAS to access the data by perform system migration
http://docs.qnap.com/nas/en/index.html?system_migration.htm
note: TS-101/201/109/209/409/409U series doesn’t support system migration
•Since the firmware is also stored on the HDD(s), its firmware version may be different to the firmware on NAS. Firmware upgrade may be required required after above operation
Obtained from this link
Maximum request length exceeded
If you are using IIS for hosting your application, then the default upload file size if 4MB. To increase it, please use this below section in your web.config –
<configuration>
<system.web>
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="1048576" />
</system.web>
</configuration>Just to add – If you are using IIS7 then you need to use below lines instead of above –
<system.webServer>
<security>
<requestFiltering>
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="1048576000" />
</requestFiltering>
</security>
</system.webServer>Note: maxAllowedContentLength is measured in bytes while maxRequestLength is measured in kilobytes, which is why the values differ in this config example.
I don’t think it’s been mentioned here, but to get this working, I had to supply both of these values in the web.config:
In system.web
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="1048576" executionTimeout="3600" />And in system.webServer
<security>
<requestFiltering>
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="1073741824" />
</requestFiltering>
</security>IMPORTANT: Both of these values must match. In this case, my max upload is 1024 megabytes.
maxRequestLength has 1048576 KILOBYTES, and maxAllowedContentLength has 1073741824 BYTES.
I know it’s obvious, but it’s easy to overlook.
It may be worth noting that you may want to limit this change to the URL you expect to be used for the upload rather then your entire site.
<location path="Documents/Upload">
<system.web>
<!-- 50MB in kilobytes, default is 4096 or 4MB-->
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="51200" />
</system.web>
<system.webServer>
<security>
<requestFiltering>
<!-- 50MB in bytes, default is 30000000 or approx. 28.6102 Mb-->
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="52428800" />
</requestFiltering>
</security>
</system.webServer>
</location>I hit a snag when uploading large files using PHP on IIS 7.5. I was getting some weird Error 404, which in most cases means the PHP script that handles the upload process was not found. I checked my server, and sure enough, the PHP script was there. I tried again to be sure, this time with a smaller file. And what do you know, it worked just fine.
This led me to believe that there was a file size restriction imposed somewhere. I’ve already modified the php.ini file to allow me to upload larger files, but still no go. So the only other thing I can think of was IIS. Apache has something like that, so it’s only obvious that the ever-so-cautious IIS would be the same.
After much research, and a couple of Google searches later, I found a simple solution involving some simple config file edits. Damn, after working with IIS for the past 6 months, I got used to not having to deal with config files. Anyway, the file you want to modify is “C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\config\applicationHost.config”. I don’t know if it makes any difference, but I’ve converted the folders that hold my PHP scripts into Applications through the IIS Manager.
So open that file up using any text editor. It was a newly installed virtual server, so I didn’t have anything other than Notepad available.
Add the following lines to the bottom of the file, making sure it’s inside the area.
Where “Default Web Site” is the name of your website, “alnet” is the name of the application, and “2147483648″ is the amount you want to set for the upload file limit in bytes. So as you can see, I’ve set my IIS to accept file sizes up to 2GB. You can add as many of this as you need. I have 3 applications, so I have three of these in my config XML script. You can also use the following line at a command prompt. Be sure to navigate to “C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv” first.
appcmd set config "Default Web Site/alnet" -section:requestFiltering -requestLimits.maxAllowedContentLength:2147483648-commitpath:apphost
Where “Default Web Site” is your website and “alnet” is the name of your application.
That’s it. Have fun and if you know of a better way to achieve the same result, let me know using the comment form.
Until next time, Wassalam.
EDIT:
An easier way to go about this, as I’ve recently discovered, is to use the IIS Manager. I know, I know. This is by far the best way to go about this, but I don’t really have that much experience with Windows Server and I’m so used to the Linux way of editing configuration files that I didn’t think to use the IIS Manager for this. Anyway, here’s how to change the file upload limit using the IIS Manager.
Open up the Server Manager and navigate to the IIS Manager. Click on your Application icon and turn your attention to the center window. Scroll down to the bottom and you will find the Configuration Editor under Management. Double-click on this and you will be presented with a bunch of settings.
Open up the drop down menu and navigate through the following; system.webServer > security > requestFiltering. Click on that and it will show you the current requestFiltering settings for your Application. Scroll down and until you find requestLimits. Expand it and there you should see maxAllowedContentLength. You can now change this value to any value you wish to set. Once you’re done, click Apply and that’s it.
Here’s a picture showing you where and what to change. At this moment, I only have the Japanese version of Windows Server available to take screenshots from, but I’m sure you get the idea.
Obtained from this link http://dnasir.com/2011/01/21/changing-the-maximum-upload-size-for-iis-7-5
ESET lanza la nueva versión de ESET NOD32 File Security compatible con Microsoft Windows Server 2012
Madrid, 28 de mayo de 2013 – ESET España, líder en protección proactiva contra todo tipo de amenazas de Internet con más de 25 años de experiencia, lanza su nueva versión de ESET NOD32 File Security compatible con Microsoft Windows Server 2012. La nueva versión, que ya está disponible para su evaluación, no solo combate todo tipo de amenazas informáticas, sino que ahora incluye una versión adaptada y especialmente optimizada para servidores con funciones importantes basadas en la edición Core de Windows Server.
ESET NOD32 File Security para Microsoft Windows Server proporciona una protección efectiva y robusta contra todo tipo de ataques de malware. Es totalmente compatible con la herramienta de gestión centralizada y administración remota ESET NOD32 Remote Administrator, por lo que cubre fácil y eficazmente las necesidades de seguridad de una red con un servidor Windows.
Además, ESET NOD32 File Security incluye otras novedades:
- Optimizado para el entorno del servidor: ha sido diseñado específicamente para cubrir las necesidades de los servidores basados en Windows y proporcionar un rendimiento óptimo con un nivel de seguridad constante.
- Árbol de configuración avanzada: cuenta con un árbol de configuración avanzada rediseñado para una navegación más intuitiva.
- eShell: ejecuta scripts para establecer la configuración o ejecutar una acción. eShell (ESET Shell) es una herramienta de interfaz por línea de comandos totalmente nueva. Además de todas las funciones y características accesibles desde la GUI (Interfaz gráfica del usuario), eShell le permite automatizar la gestión de los productos de seguridad ESET.
- Exclusiones automáticas: detección automática y exclusión de archivos críticos del servidor para un funcionamiento óptimo.
Otras características clave y beneficios
- Protección antivirus: contra todo tipo de amenazas de Internet, como rootkits, gusanos y virus.
- Autodefensa: nueva tecnología que evita que las soluciones de seguridad ESET sean modificadas o desactivadas por el malware.
- Solución eficiente de problemas: incorpora herramientas avanzadas para solucionar diversas incidencias, como ESET SysInspector para un diagnóstico del sistema y ESET SysRescue para crear un CD de rescate autoarrancable.
- Implementación sin problemas: garantiza una instalación rápida y sencilla de ESET NOD32 File Security para Microsoft Windows Server.
- Tecnología única: con métodos sofisticados para la detección de malware, el motor de análisis ThreatSense® proporciona un nivel de seguridad óptimo para la información de su empresa.
- Actualizaciones periódicas: las actualizaciones de la base de firmas de virus, así como las mejoras técnicas de los laboratorios ESET, se descargan e instalan sin provocar ninguna interrupción en su funcionamiento normal.
- Bajo consumo de recursos: ESET NOD32 File Security para Microsoft Windows Server utiliza el mínimo posible de recursos y deja libre más memoria y potencia de la CPU para las tareas importantes del sistema.
- Informes detallados: manténgase informado de la seguridad de su empresa con registros de seguridad detallados, información acerca del estado de la protección y notificaciones del sistema.
ESET File Security para Microsoft Windows Server está disponible para su prueba a través de la página web de ESET y se puede adquirir a través de la red de distribuidores de ESET NOD32 España o bien a través de su tienda online.


Cómo hacer capturas de pantalla en OS X
Cómo hacer capturas de pantalla en OS X

Una de las preguntas más frecuentes de quien se acaba de pasar a Mac, es cómo hacer capturas de pantalla en OSX. En PC hay una tecla llamada ‘Imprimir pantalla’, con la que podemos pasar lo que vemos en la pantalla al portapapeles para después pegarlo en Paint por ejemplo. Pero en Mac esa tecla no existe, ¿cómo hacemos una captura?
Es aún más sencillo, hay cuatro maneras:
Shift + Comando + 3
Con esta combinación de teclas, obtendremos automáticamente una captura de toda nuestra pantalla, y el archivo se creará en el escritorio con el nombre ‘Imagen 1.png’
Shift + Comando + 4
De esta otra manera, el cursor cambia a un punto de mira que podemos arrastrar para seleccionar a mano qué parte de la pantalla queremos capturar. También se crea un archivo en el escritorio con el nombre ‘Imagen 1.png’
Shift + Comando + 4, y después barra espaciadora
Si después de hacer la combinación de teclas anterior pulsamos la barra espaciadora, el cursor cambiará a una cámara fotográfica, de manera que podremos elegir qué ventana en concreto queremos capturar. La imágen capturada aparecerá en nuestro escritorio con el nombre ‘Imagen 1.png’.
Con el programa ‘Instantánea’

Dentro de nuestra carpeta ‘Aplicaciones’, en la carpeta ‘Utilidades’, podemos encontrar el programa ‘Instantánea’. Con él podremos hacer lo mismo que con los atajos de teclado anteriores, pero al capturar, la imágen se abre en una ventana y podemos imprimirla o guardarla donde queramos. Además hay un modo más: ‘Capturar pantalla con temporizador’. Funciona igual que las cámaras de fotos, hay una cuenta atrás de unos segundos y saca la foto.
Por último, cuando capturamos con las tres combinaciones de teclas, si pulsamos también la tecla ‘Control’, en vez de generar un archivo en el escritorio, la foto quedará guardada en el portapapeles para que la peguemos donde queramos.
Obtenido de http://www.pasateamac.com/como-hacer-capturas-de-pantalla-en-os-x/
Madrid, 9 de mayo de 2013 – ESET, el líder en protección proactiva con más de 25 años de experiencia, anuncia el lanzamiento de ESET Secure Authentication, nuevo sistema de autenticación con doble factor y contraseña de un solo uso para redes corporativas. La solución es muy sencilla de utilizar y proporciona una capa adicional de seguridad en el proceso de autenticación de los usuarios en sus teléfonos móviles, además de la validación habitual con usuario y contraseña.
ESET Secure Authentication es compatible con iPhone, Android, Blackberry, Windows Phone 7 y 8, Windows Mobile y sistemas basados en J2EE. La solución soporta autenticación basada en mensajes de texto, por lo que se puede utilizar incluso en teléfonos antiguos que no puedan instalar la aplicación.
Cada vez son más las incidencias que tenemos relacionadas con la seguridad y privacidad de nuestros dispositivos móviles, ya que hay una alta probabilidad de perderlos o de que sean robados. Si no protegemos los dispositivos, corremos el riesgo de que cualquiera pueda acceder a toda nuestra información como si fuéramos nosotros mismos. Este problema puede ser mayor si el dispositivo lo usamos para trabajar e incluye los accesos a los diferentes servicios de la red corporativa.
ESET Secure Authentication permite el acceso seguro a las redes corporativas desde estos dispositivos. Su funcionamiento es muy sencillo: cuando el usuario necesita validarse, obtiene una contraseña, que sirve para un solo uso y que garantiza el acceso al usuario desde su dispositivo móvil con mayor protección de la habitual.
ESET Secure Authentication forma parte del catálogo de soluciones de ESET con el que la compañía quiere ayudar a sus clientes a proteger los datos corporativos en tecnologías móviles.
“ESET extiende su catálogo de soluciones de tecnología de seguridad para todos los clientes. Estamos respondiendo a la creciente necesidad de asegurar los activos en compañías pequeñas y medianas. ESET Secure Authentication es ideal para pymes que no pueden realizar una gran inversión en soluciones de autenticación de dos factores o que no están interesadas en desplegar soluciones más complejas”, afirma Josep Albors, director del Laboratorio de ESET NOD32 España.
Ventajas y beneficios
ESET Secure Authentication es fácil de instalar y configurar. La solución se integra por defecto con la mayoría de servicios y protocolos más utilizados. Ofrece protección para Outlook Web Access/App y RADIUS. El nuevo producto ha sido especialmente revisado y probado con Windows Server (2003, 2003 R2, 2008, 2008 R2 y 2012).
Soporte para las plataformas móviles más populares: los usuarios utilizan mayormente dispositivos modernos que cuentan con sistemas como iPhone, Android, BlackBerry, Windows Phone 7 y 8, Windows Mobile y teléfonos basados en J2ME. La autenticación se realiza mediante una aplicación que el usuario descarga en su terminal de manera sencilla. Una vez instalada, permite al usuario generar contraseñas seguras de un solo uso. También se puede obtener las claves enviando un mensaje SMS en el caso de que el dispositivo del usuario no soporte la instalación de aplicaciones.
Entorno de gestión y mantenimiento conocido (MMC y ADUC plugin): los administradores pueden gestionar ESET Secure Authentication desde entornos tan familiares como Active Directory y Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
Soluciona el problema de:
Contraseñas débiles que pueden ser interceptadas.
Contraseñas creadas por el usuario que no son una combinación aleatoria de varios caracteres y símbolos, pudiendo ser adivinadas fácilmente.
Reutilización de contraseñas destinadas para acceder a la información de la empresa en cuentas privadas.
Contraseñas que contienen información personal del usuario, por ejemplo, nombre, fecha de nacimiento, etc.
Modelos simples para crear nuevas contraseñas tales como «peter1», «peter2», etc.
Acceso a la información de la empresa en caso de pérdida o robo de dispositivos móviles e itinerantes.
Configuración automática: la instalación de la aplicación en el dispositivo móvil es simple y sencilla, ya que el usuario solo necesita hacer clic en un enlace de un mensaje de texto.
Más información sobre ESET Secure Authentication en http://www.eset.es/empresas/eset-secure-authentication.
Installing SQL Server 2008 Reporting Services on Failover Cluster in already clustered instance
A way of achieving SQL Server 2008 High Availability is installing SQL Server on top of Windows Server 2008 failover cluster. Only Database Engine Services and Analysis Services are cluster aware while SQL Server 2008 Reporting Services and shared components (Integration Services, Management Studio, Business Intelligence Development Studio etc.) are not.
Checks if the selected instance name is already used by an existing
cluster-prepared or clustered instance on any cluster node.Failed – The instance selected for installation is already installed and
clustered on computer . To continue, select a different instance to
cluster.»
- Reporting Services running on an Active-Passive cluster handle requests on each cluster node on which the service is deployed.
- Report server must be configured to use SQL failover cluster virtual name to connect to the report server database. This is because it is hosted on a SQL Server that is part of a failover cluster. If not, the report server will be unable to connect to the report server database if a failover occurs.
This solution provides the highly available Reporting Services with default SQL server instance and uses already deployed hardware. It is not substitute for a true Scale-out deployment of the Reporting Services, but a way of achieving high availability (we just used the existing high availability platform). Scale-out enables you to increase the number of users who can concurrently access/invoke reports and improves the availability of the report server.
Obtained from this link
Other link
Enabling Jumbo Frame support in Hyper-V Server 2008 R2 (or Windows Server Core) has proven to be a bit of an adventure. It really just involves setting the MTU size, but it has to be done in the OS (to affect the TCP/IP stack) as well as the network cards’ driver. Since Core versions of Windows do not have a network control, setting the MTU on the cards proves to be a bit of a trick. This is what I had to do to enable Jumbo Frames on several iSCSI nics, and since it differs for Intel vs Broadcom adapters, there are two procedures.
I should point out that this does not address configuring the network switch that these nics are attached to. That is a whole ‘nother can of worms, but suffice it to say that the switch must not only support Jumbo Frames but have that support enabled, along with a whole host of other settings.
Enable Jumbo Frames on the OS
The first thing you need to do is make sure that your server will allow jumbo frames. You do this by setting the MTU on your adapters to 9000. The easiest way to do this is by running a netsh command on each adapter you want to use Jumbo Frames.
Get a list of interface names by running “netsh int show int”
Admin State State Type Interface Name |
------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
Enabled Disconnected Dedicated Local Area Connection 2 |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Bcom-GB3-iSCSI-A |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Local Area Connection |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Local Area Connection 3 |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Local Area Connection 4 |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Bcom-GB4-iSCSI-B |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Intel-GB1-Guest-B |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Bcom-GB2-Guest-A |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Intel-GB2-Guest-C |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Bcom-GB1-Mgmnt |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Intel-GB3-iSCSI-C |
Enabled Connected Dedicated Intel-GB4-Migration |
In this case I have already re-named the Interfaces that I intend to use for iSCSI. You might just see a whole list of “Local Area Connection” interfaces. You can use ipconfig or netsh to further identify which ones you want to use.
Now for each interface you want jumbo frames enabled, run this command:
netsh int ipv4 set subint “” mtu=9000 store=persistent
Now you have to configure Jumbo Frames in the driver for each interface.
Enable Jumbo Frames on Intel cards
The Intel driver stores it’s “Jumbo Frame” settings in the registry. Thankfully, Hyper-V Server (and Windows Core) comes with Regedit, so you can just launch that from command line (regedit.exe) and browse to the following key:
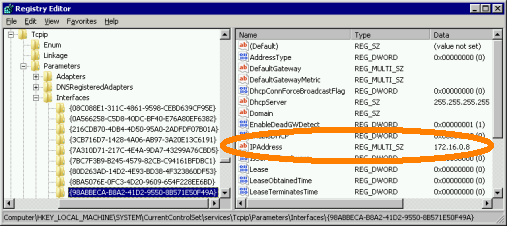
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesTcpipParametersInterfaces |
Here you will see all the network interfaces listed by GUID. I have found that the easiest way to determine which GUID is which adapter is by finding the IP address and being able to correlate it to the right Interface name.
At this point you should start making a list to help keep things straight. Copy the GUID into notepad and list the IP address next to it and do this for each card you want to configure. So for this server, my list looks like this:
SERVERNAME {7A310D71-217C-4E4A-9DA7-43299A76CBD5} 172.16.0.9 |
SERVERNAME {7BC7F3B9-B245-4579-82CB-C94161BFDBC1} 172.16.0.7 |
SERVERNAME {8BA5076E-0FC3-4D20-9609-654F228EE6BD} 172.16.0.6 |
SERVERNAME {98ABBECA-B8A2-41D2-9550-8B571E50F49A} 172.16.0.8 |
Now we have to navigate to a new registry key to configure the driver. Go here:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlClass{4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318} |
Here you will again see a list of all network interfaces, only this time they are under 4 digit identifiers. From here, search for the GUID that you copied to your list and you should find it as the “NetCfgInstanceId” key of one of the adapters. Once found, it’s not a bad idea to update your list to keep track of what’s what. Mine looks like this now:
SERVERNAME {7A310D71-217C-4E4A-9DA7-43299A76CBD5} 172.16.0.9 0009 Intel |
SERVERNAME {7BC7F3B9-B245-4579-82CB-C94161BFDBC1} 172.16.0.7 0005 Broadcom |
SERVERNAME {8BA5076E-0FC3-4D20-9609-654F228EE6BD} 172.16.0.6 0004 Broadcom |
SERVERNAME {98ABBECA-B8A2-41D2-9550-8B571E50F49A} 172.16.0.8 0008 Intel |
Scroll up to find the “*JumboPacket” key and double click it to change the default value of 1514 to 9014. Note the extra 14 bytes here represents packet headers that normally are not counted in MTU size.
Repeat this for each Intel adapter you need to configure, and then reboot the server for the setting to take effect.
Enable Jumbo Frames on Broadcom cards
First make sure you have the latest Broadcom drivers. Make sure you get the 2008 R2 x64 set.
If you haven’t already, then download and install the driver and then reboot the host. Note: Make sure you migrate any existing guest servers off the host before you install the drivers. The temporary outage of the card due to the update seems to make a failover cluster angry.
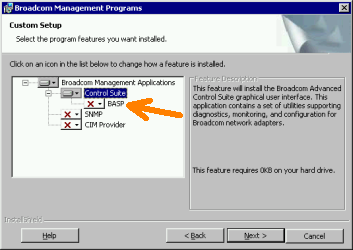
Now get the Broadcom Management Application suite. Again, get the x64 set from the same page.
Install the management app. I opt’d not to install the BASP component (see screenshot below) since we do not want failover or teaming in this scenario. It’ll likely warn you that you need the dotNet Framework 2.0 and you should be able to ignore this because the installer just does not recognize the “Core” framework, but the application still runs. To make sure you do in fact have the framework installed, run “oclist | findstr /i netfx” and look for a line stating that NetFx is installed. For example, “Installed:NetFx2-ServerCore”. If not, you can install it by running “start /w ocsetup NetFx2-ServerCore” or instead you can install dotNet 3.0 and 3.5 by running “start /w ocsetup NetFx3-ServerCore”.
From C:Program FilesBroadcomBACS run “BACSCLi” to run in interactive mode. It will show you a list of all network adapter drivers installed. You only care about the “NDIS” adapters so enter “list ndis” and you’ll see something like this:
C MAC Dev Type Name |
- ------------ -------- ---------------------------------------------------- |
0 001B214285B8 NDIS [0000] Intel(R) Gigabit ET Quad Port Server Adapter |
1 001B214285B9 NDIS [0007] Intel(R) Gigabit ET Quad Port Server Adapter #2 |
2 001B214285BC NDIS [0008] Intel(R) Gigabit ET Quad Port Server Adapter #3 |
3 001B214285BD NDIS [0009] Intel(R) Gigabit ET Quad Port Server Adapter #4 |
4 0026B9429866 NDIS [0002] Broadcom BCM5709C NetXtreme II GigE (NDIS VBDClient) |
5 0026B9429868 NDIS [0003] Broadcom BCM5709C NetXtreme II GigE (NDIS VBDClient) #2 |
6 0026B942986A NDIS [0004] Broadcom BCM5709C NetXtreme II GigE (NDIS VBDClient) #3 |
7 0026B942986C NDIS [0005] Broadcom BCM5709C NetXtreme II GigE (NDIS VBDClient) #4 |
If you did the Intel configuration you’ll notice the four digit number in square braces of the Name field matches the ControlClass registry key.
Use some combination of “ipconfig /all” in another window or CtxAdmTools’ Visual Core Configurator 2008 or the four digit registry code to identify the adapter that you want to configure. In this example we want Connection #6. Select it by using “select 6” or whatever number is in the “C” column that matches your adapter. Now validate that you have selected the correct adapter by reviewing some of its details. Run “info” to see it’s MAC/IP, etc.
Vital Signs |
----------- |
MAC Address: : 00-26-B9-42-98-6A |
Permanent MAC Address: : 00-26-B9-42-98-6A |
IPV4 Address : 172.16.0.6 |
Link Status : UP |
Duplex: : Full |
Speed(in Mbps): : 1000 |
Offload Capabilities : TOE,LSO,CO,RSS |
Mtu : 1500 |
Driver Information |
----------- |
Driver Status: : Loaded |
Driver Name: : bxnd60a.sys |
Driver Version: : 5.0.13.0 |
Driver Date: : 07/30/2009 |
Notice the MTU setting is set to 1500 by default. Now run “cfg advanced” to list its advanced properties.
Advanced |
-------- |
Ethernet@WireSpeed: Enable (Default) |
Flow Control: Disable |
IPv4 Checksum Offload: Tx/Rx enabled (Default) |
IPv4 Large Send Offload: Enable (Default) |
IPv6 Checksum Offload: Tx/Rx enabled (Default) |
IPv6 Large Send Offload: Enable (Default) |
Interrupt Moderation: Enable (Default) |
Jumbo MTU: 1500 (Default) |
Locally Administered Address: Not Present (Default) |
Number Of RSS Queues: 8 (Default) |
Priority & VLAN: Priority & VLAN enabled (Default) |
Receive Buffers: 750 (Default) |
Receive Side Scaling: Enable (Default) |
Speed & Duplex: Auto (Default) |
TCP Connection Offload (IPv4): Enable (Default) |
TCP Connection Offload (IPv6): Enable (Default) |
Transmit Buffers: 1500 (Default) |
VLAN ID: 0 (Default) |
Wake Up Capabilities: Both (Default) |
Run “cfg advanced “Jumbo MTU”=9000” to set Jumbo frames to 9000 bytes. Note that you do not have to account for the 14 bytes of header data here. It’ll take a few seconds to apply the change but you should not need to reboot (yay!). You can now run “cfg advanced” and “info” to list the settings and ensure that the MTU is in fact set to 9000.
You should also enable Flow Control for Transmit (Tx) and Receive (Rx). With the correct adapter already selected, run “cfg advanced “Flow Control”=”Rx & Tx enabled””.
Once that is complete you can enter “q” to exit BACScli or start over using “list ndis” and select another interface to configure. You can also use this utility to select non-Broadcom adapters to display some of their info like MTU size.
Testing Jumbo Frames
To test if Jumbo Frames are working you can ping another host target that also supports Jumbo Frames. The easiest way that I have found to do this was to just change the IP of your test NIC and your test target NIC to something that no other adapter has. This is because there is no way to tell windows specifically what NIC to send traffic over, so setting the NIC’s to their own network ip space is the only way to ensure that the ping traverses a particular adapter.
For example, I changed the source test nic to 172.16.1.4 and the target to 172.16.1.8 and no other adapters on either host saw set in the 172.16.1.* range.
First try a normal “ping 172.16.1.8” and it should work fine. Then use “ping -f -l 6000 172.16.1.8” to test jumbo frames and it should also work, only this time you’ll see it sending 6000 bytes instead of 32.
So that about covers it. I had to do this for each of the 32 iSCSI nics spread across the 8 host servers, but it works! You should be aware that if you do a driver update or if you share a NIC with a virtual network (as a Hyper-V Host) your settings may be lost and you’ll have to go through this again.
Obtained from this link http://mrshannon.wordpress.com/2010/01/13/jumbo-frames-on-hyper-v-server/#comment-13
Since there are multiple ways to gather this in the Windows 2008 and 2008R2 I thought this might be helpful to outline this for the different platforms and how to gather this for fellow ARR troubleshooters.
Windows 2008
1. Start the Tracing . From a command prompt run the following command:
netsh winhttp set tracing trace-file-prefix=»C:TEMPWinHttpLog» level=verbose format=hex state=enabled max-trace-file-size=1048576000
2.Recycle the IIS Application Pool.
3. Reproduce the issue.
4. Stop the Tracing. From a command prompt run the following command:
netsh winhttp set tracing state=disabled
5. Review the trace with Notepad or any Text editor.
NOTE: The Identity of the IIS application pool will require write access to the log location c:Temp in this example:
This type of tracing is process bitness specific, so if you are looking at a 32 bit process running from 64 bit OS, you need to use: c:windowssyswow64cmd.exe, rather than using the regular 64 bit cmd.exe (start a run a cmd.exe)
Windows 2008 R2
Method 1
This method will output the Winhttp API calls , but not raw data for network communication. From a command prompt run the following command:
1. Start the tracing
netsh winhttp set tracing trace-file-prefix=»C:TempTest3″ level=verbose format=hex
netsh winhttp set tracing output=file max-trace-file-size=512000 state=enabled
2.Recycle the IIS Application Pool.
3. Reproduce the issue.
4. Stop the Tracing. From a command prompt run the following command:
netsh winhttp set tracing state=disabled
5. Review the trace with Notepad or any Text editor.
NOTE: The Identity of the IIS application pool will require write access to the log location c:Temp in this example:
This type of tracing is process bitness specific, so if you are looking at a 32 bit process running from 64 bit OS, you need to use: c:windowssyswow64cmd.exe, rather than using the regular 64 bit cmd.exe (start a run a cmd.exe)
Method 2
To get the raw data communication at network layer and the Winhttp Api calls.
1. Start the tracing: From a command prompt run the following command:
netsh trace start scenario=InternetClient capture=yes report=yes
Note the etl file location for example:
Trace File: C:Users
AppDataLocalTempNetTracesNetTrace.etl
2.Recycle the IIS Application Pool.
3. Reproduce the issue.
4. Stop the tracing: From a command prompt run the following command:
netsh trace stop
5. Read the Trace by opening it in Netmon 3.4.
Method 3
The ETW format for winhttp API is available on windows 2008 R2 and win7 via the Event Viewer
1. Open event viewer. Go to “View” menu –> make sure “Show Analytic and debug logs” is checked.
2. Open “Applications and Services logs” — > Open “Microsoft” — > Open “Windows –> Winhttp –> Diagnostic.
3. Highlight “Diagnostic” under Winhttp tree and right click mouse, then click “enable log”.
4. Reproduce the issue then you can review the logs.
References
Netsh Commands for Network Trace in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd878517(v=WS.10).aspx
Obtained from this link
When working with ARR deployments one of the errors you might see is 502.3 Bad Gateway. The 502.3 means while acting as a proxy ARR was unable to complete the request to the upstream server and subsequently send a response back to the client. This can happen for multiple reasons including , failure to connect to the server , no response from the server, or server took too long to respond (time out).
For the purposes of this post we are going to look at a timeout error and the data that can be gathered to help isolate the cause.
If you are looking at this post then you probably have already seen this error or something similar. This is shown in the browser when detailed errors are enabled in IIS.
Another way to identify the source of the 502.3 is with Failed Request Tracing logs in IIS configured to capture Status code 502.
From the message the key details are the ErrorCode which you can use to map to to the Winhttp error message, which in this case is ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT ( Reference WinHttp Error Codes). You will also see in the next line that this is translated to “The operation timed out”. Note that both the 0x80072ee2 and 2147954402 map to the same error ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT.
Now that we know its a timeout we need to determine what type of timeout occurred. Here is a list of the timeouts that can occur in Winhttp ( which if you haven’t guessed already is what ARR uses to proxy requests)
- ResolveTimeout : This occurs if name resolution takes longer than the specified timeout period.
- ConnectTimeout : This occurs if it takes longer than the specified timeout period to connect to the server after the name resolved.
- SendTimeout : If sending a request takes longer than this time-out value, the send is canceled.
- ReceiveTimeout : If a response takes longer than this time-out value, the request is canceled.
To identify what type of timeout we can use Winhttp’s built in logging,These can be enabled from the command line on the ARR server using NETSH.
- Winhttp Traces:
Following the example below you can search your log for WinHttpOpenRequest to find your request. The calls to WinHttpSetTimeouts are setting the 4 timeout values based on your ARR time settings found in the Proxy Configuration page of your ARR Server Farm or in the Server Proxy settings. Next we find WinHttpSendRequest then WinHttpReceiveResponse , so we know we are now in the receive stage. Finally we see that the error in is in RecvResponse so we know this is a ReceiveTimeout. For a different failure such as ResolveTimeout we would not see the log make it to WinHttpReceiveResponse and the failure would be logged earlier.
10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpOpenRequest(0x35a970, "GET", "/sleep/default.aspx", "HTTP/1.0", "", 0x0, 0x00000080) ………… 10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpSetTimeouts(0x2e42d80, 30000, 30000, 30000, 30000) 10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpSetTimeouts() returning TRUE …………10:23:45.100 ::WinHttpSendRequest(0x2e42d80, "Accept: */*rnAccept-Encoding: gzip, deflaternAccept-Language: en-CArnHost: contoso.com", 479, 0x0, 0, 0, 24794c0) …………10:24:15.397 ::Completing WinHttpSendRequest() with success; Request Handle = 02E42D80, Context = 024794C0, Buffer = 00000000 (0x0), Buffer Length = 0 10:24:15.397 ::WinHttpReceiveResponse(0x2e42d80, 0x0) ………… 10:24:15.397 ::sys-recver failed to receive headers; error = ? (1460) 10:24:15.397 ::ERROR_WINHTTP_FROM_WIN32 mapped (?) 1460 to (ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT) 12002 10:24:15.397 ::sys-recver returning ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT (12002) from RecvResponse() 10:24:15.397 ::sys-req completes recv-headers inline (sync); error = ERROR_WINHTTP_TIMEOUT (12002)
Now that we know this is receive timeout we can look at the content server and see how long the request took.
-
IIS logs on the Content Server:
Examine the IIS logs on the content server and check the sc-status and sc-win32-status and time-taken fields. This will give you an idea of whether the request processed successfully ( sc-status = 200) and the time-taken to see if this exceeds your ARR timeout and if this is the expected execution time for your web page . You can determine from this whether you need to troubleshoot a long running application or simply increase the ARR timeout settings. Checking the Win32 field for errors such as 1236 (ERROR_CONNECTION_ABORTED) or 64 (ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED) indicate that something happened on the network layer such as a connection reset.
Using our example the IIS logs here show that the Request took ~35 seconds (time-taken=35615) , the request was processed successfully on the server (sc-status=200) , but there was a problem sending the request (sc-win32-status=64) which means the connection was gone when the content server tried to send the request. This was because the client (ARR) has already timed-out and closed the TCP connection.
#Software: Microsoft Internet Information Services 7.0 #Version: 1.0 #Date: 2010-06-23 20:11:33 #Fields:date time cs-method cs-uri-stem s-port sc-status sc-substatus sc-win32-status time-taken 2010-06-23 20:11:33 GET /sleep/default.aspx 80 200 0 64 35615
Summary
So in this case we can see that the request took >35 seconds which is longer than the default timeout in ARR. When this occurs ARR ( or Winhttp underlying ARR) will close the connection to the content server which is what cause the Win32 error 64.
Now its up to you to determine whether its acceptable that your page is running for 35 seconds and you just need to increase time outs in ARR.
Since the application issues are beyond the scope of this blog I’ll leave you with two command lines for setting ARR timeouts for either a Server Proxy configuration or Server Farms.
Server Proxy : appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/proxy /timeout:»00:00:45″ /commit:apphost
Server Farm : appcmd.exe set config -section:webFarms /[name=’ArrFarm’].applicationRequestRouting.protocol.timeout:»00:00:45″ /commit:apphost
References
Netsh Commands for Windows Hypertext Transfer Protocol (WINHTTP)
Failed Request Tracing in IIS (FREB)
UPDATE : New Post for Winhttp Tracing Methods
ARR on IIS.NET